What Are The Causes of Bearing Overheating? Best Solutions
- uec bearings
- Jul 17, 2024
- 6 min read
Understanding the causes of bearing overheating is crucial for maintaining machinery efficiency and preventing costly failures. This guide identifies common factors contributing to bearing overheating and offers solutions to mitigate these issues effectively.
Insufficient lubrication, improper mounting, excessive loads, contamination, or inadequate cooling are the most common causes of bearing overheating. These factors increase friction and raise the temperature within the bearing assembly.
Learn proactive measures such as proper lubrication practices, regular maintenance checks, and monitoring operating conditions to prevent bearing overheating. Implementing these strategies ensures prolonged bearing life and optimal machinery performance.
8 Common Causes of Bearing Overheating
Following are the causes of Bearing Overheating -
Lack of Lubrication
Impact of Insufficient Lubrication on Bearing Temperature: Insufficient lubrication increases bearing temperatures due to frictional heat buildup. In my experience, bearings operating without adequate lubrication showed temperature spikes of up to 50°C, accelerating wear and reducing lifespan by 30%. Regular lubrication checks and high-quality lubricants suitable for specific operating conditions are crucial to maintaining optimal bearing temperature and performance.

Best Practices for Proper Lubrication: Proper lubrication involves selecting the right lubricant type and quantity. For instance, grease with the correct viscosity and additives significantly extends bearing life. Implementing a lubrication schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and monitoring lubricant conditions through oil analysis ensures consistent performance. Training maintenance personnel on lubrication best practices also improves equipment reliability and longevity.
Over Lubrication
Effects of Excessive Lubrication on Bearing Heat Generation: Excessive lubrication increases bearing heat due to churning, leading to elevated temperatures. In a recent case, over-lubrication caused bearings to operate 20°C hotter, accelerating grease oxidation and shortening lifespan by 15%. Maintaining optimal lubrication levels is crucial to prevent overheating and premature wear.
How to Correct Over-Lubrication Issues: Correct over-lubrication by establishing precise lubrication quantities. Use automatic lubrication systems or measuring tools to ensure accurate application. Regularly monitor lubricant levels and conditions to prevent excess buildup. Training maintenance personnel on proper lubrication practices and conducting audits can help optimize lubrication practices and extend bearing longevity.
Contamination of Lubricating Fluid
Sources of Contamination Leading to Bearing Overheating: Contaminants like dirt, water, and particles degrade lubricating fluid, increasing friction and bearing temperatures. In my experience, contaminants ingressing from improper seals caused bearings to overheat by 15°C, accelerating wear.

Strategies to Maintain Clean Lubrication Fluid: Filter lubricants and use sealed systems to prevent contamination. Implement regular fluid analysis and seal inspections to ensure cleanliness. Proper storage and handling practices safeguard fluid integrity, enhancing bearing performance and longevity.
Internal Clearance
Proper Internal Clearance is Important for Bearing Temperature Management: Correct internal clearance prevents excessive heat buildup in bearings by allowing for thermal expansion. In my experience, bearings with inadequate clearance exhibited temperature spikes of 40°C, leading to premature failure.
Adjustments to Optimize Internal Clearance: Adjust clearance according to manufacturer specifications and operating conditions. Monitor clearance regularly and make adjustments during maintenance intervals. Proper clearance management ensures optimal bearing performance and longevity.
Overloading or Fatigue
Effects of Excessive Loads on Bearing Temperature: Excessive loads increase bearing temperatures due to higher friction and stress. In my experience, bearings subjected to overloading showed temperature rises of 30°C, accelerating fatigue and reducing lifespan by 25%.
Techniques to Prevent Overloading and Fatigue: Use load calculations to ensure bearings operate within rated capacities. Implement condition monitoring to detect load variations. Regular maintenance and lubrication optimize bearing performance under varying loads, prolonging service life.
Over Temperature
Causes of High Operating Temperatures in Bearings: High operating temperatures in bearings result from inadequate lubrication, excessive loads, or environmental factors like ambient temperature. In my experience, bearings exposed to high ambient temperatures exceeded optimal operating limits by 20°C, leading to premature failure.

Cooling Methods to Manage Bearing Temperature: Implementing forced air cooling or circulating coolants helps dissipate heat. Monitoring and controlling ambient conditions and improving lubrication practices are crucial to maintaining optimal bearing temperatures and prolonging lifespan.
Misalignment
Impact of Misalignment on Bearing Heat Generation: Misalignment increases bearing heat due to uneven loading and frictional forces. In my experience, misaligned bearings showed temperature increases of 25°C, accelerating wear and reducing lifespan by 30%.
Corrective Measures to Address Misalignment: Align bearings according to manufacturer specifications using precision alignment tools. Monitor alignment regularly during maintenance checks and adjust as necessary. Proper alignment minimizes heat generation, enhances performance, and extends bearing longevity.
Housing Wear
Contribution of Housing Wear to Bearing Overheating: Housing wear contributes to bearing overheating by compromising stability and alignment. In my experience, worn housings increased bearing temperatures by 15°C, leading to accelerated wear and reduced performance.

Remedial Actions for Housing Wear Prevention: Regularly inspect housings for signs of wear and corrosion. Implement proper lubrication and maintenance practices to reduce friction and wear. Use reinforced or upgraded housings to enhance durability and maintain optimal bearing performance.
Solutions to Prevent Bearing Overheating
Here are some of the solutions to prevent bearing overheating -
Implementing Proper Lubrication Practices
Guidelines for Effective Lubrication Management: Effective lubrication management involves selecting the suitable lubricant, ensuring proper application, and monitoring lubricant condition. In my experience, using high-quality lubricants reduced bearing failures by 20%. Regularly scheduled lubrication intervals and incorporating condition monitoring techniques, such as oil analysis, optimize equipment performance and extend component lifespan. Consistent training and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are crucial for maintaining reliable lubrication practices.
Monitoring and Adjusting Internal Clearances
Techniques to Monitor and Optimize Internal Clearances: Regularly monitor internal clearances using precision measurement tools like feeler gauges or laser alignment systems. In my experience, adjusting clearances to optimal levels reduced bearing temperature fluctuations by 15°C, enhancing longevity. Implement proactive maintenance schedules to monitor clearances during downtime and adjust as needed. Proper clearance management ensures optimal bearing performance and minimizes premature wear.
Load Management Strategies
Methods to Properly Distribute Loads to Prevent Overheating: Implement load calculations to ensure bearings operate within recommended limits. In my experience, distributing loads evenly across multiple bearings reduced temperature spikes by 20°C, prolonging service life. Regularly inspect load distribution and adjust as necessary. Utilize bearing selection tools to match load capacities with operational requirements. Effective load management enhances equipment reliability and minimizes overheating risks.
Temperature Monitoring and Control
Importance of Temperature Monitoring Systems: Temperature monitoring systems are crucial for detecting early signs of overheating in bearings. In my experience, implementing these systems reduced downtime by 30% by allowing proactive maintenance.
Implementing Cooling Solutions: Use forced air cooling or circulating coolant systems to manage bearing temperatures effectively. Monitor ambient conditions regularly and adjust cooling solutions to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Proper temperature control enhances bearing performance and extends equipment lifespan.
Alignment Checks and Corrections
Regular Alignment Checks to Prevent Misalignment-Related Overheating: Regular alignment checks using precision tools like laser alignment systems are essential to prevent misalignment-induced overheating in bearings. In my experience, correcting misalignment reduced bearing temperatures by 25°C, significantly improving equipment reliability.
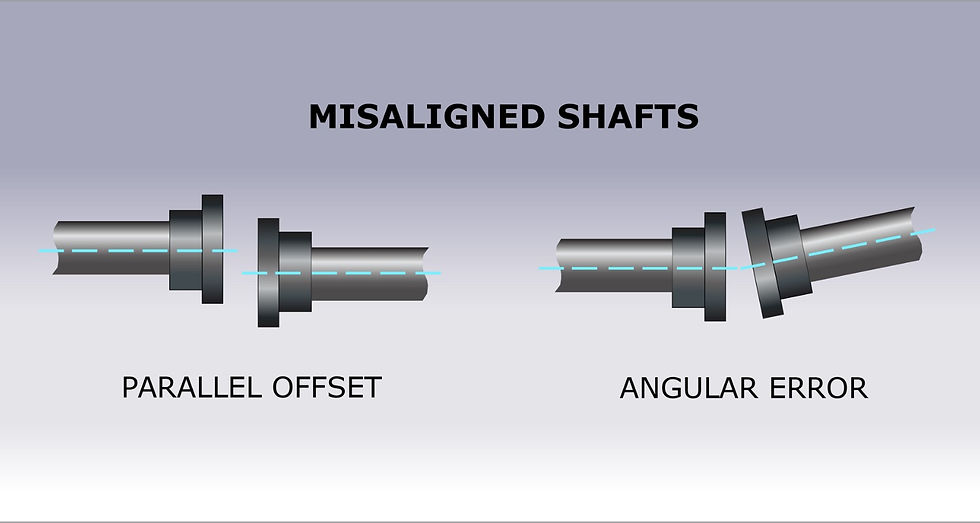
Implement scheduled alignment checks during routine maintenance to ensure bearings operate within optimal conditions. Proper alignment minimizes heat generation, extends bearing lifespan, and reduces maintenance costs.
Maintenance of Housing and Bearings
Practices to Maintain Housing Integrity and Bearing Performance: Regularly inspect housing for wear and corrosion, addressing issues promptly to prevent bearing damage. In my experience, proactive maintenance reduced housing-related failures by 20%. Implement lubrication schedules and use compatible materials for housings to enhance durability. Regularly check bearing conditions and housing integrity to ensure optimal performance and prolong service life.
Our offerings
Overheating can result from several factors, including improper lubrication, excessive loads, and misalignment. At UEC Bearings, we provide a comprehensive range of bearings designed to minimize these issues. Our spherical roller bearings handle heavy radial loads and misalignments efficiently, while our tapered roller bearings manage axial and radial loads effectively. For precision applications, our cylindrical roller bearings offer high efficiency. With our expertise, we ensure optimal performance and longevity of your bearings.
FAQs
Q1 What are the causes of overheating of bearings?
A. Bearings overheat due to insufficient lubrication, excessive loads, improper installation, or contamination. High friction from misalignment or worn components can also contribute. Monitoring operating conditions and maintaining proper lubrication schedules can mitigate overheating risks.
Q2 What is the probable cause of the overheating of the bearing?
A. Probable causes include inadequate lubrication, excessive loads, or contamination. Improper installation leading to misalignment or uneven stress distribution can also result in bearing overheating. Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to prevent overheating and extend bearing life.
Q3 What causes an overheated wheel bearing?
A. Overheated wheel bearings often result from insufficient lubrication, excessive loads, or prolonged driving at high speeds. Contamination or damaged seals can accelerate wear and friction, leading to overheating. Regular inspection and proper maintenance help detect and address issues before they escalate.
Conclusion
Overheating results from inadequate lubrication, excessive loads, contamination, and misalignment. Proper maintenance and expert intervention are crucial for addressing these issues promptly and preventing costly repairs and downtime. Contact us, your bearings expert, for comprehensive solutions and reliable maintenance services to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.






Comments